Views lets you filter query results using custom fields. This way, you can load the exact content you need, depending on custom field values.
You can filter by as many custom fields as you need, filter by hard-coded values or let visitors choose filter values.
On this page:
1. Inputs Reference
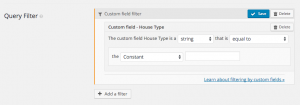
In the Query Filter section of a View, click Add a filter. You will see different filter options. Choose a custom field and you will get to this dialog:
This dialog includes a wealth of filtering options. Let’s go through them.
Comparison function
The comparison function is the function that Views will use to compare between the custom-field value and the filter value.
Values for this field correspond to the MySQL comparison functions:
| Comparison function | Arguments | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| = | Single value | Checks if the custom field value exactly matches the compare value |
| != | Single value | Checks if the custom field value doesn’t match the exact compare value |
| > | Single value | Checks if the custom field value is greater than the compare value |
| >= | Single value | Checks if the custom field value is greater than, or equals, the compare value |
| < | Single value | Checks if the custom field value is less than the compare value |
| <= | Single value | Checks if the custom field value is less than, or equals, the compare value |
| LIKE | Single value | Checks if the custom field value is similar to the compare value, using MySQL LIKE operator |
| NOT LIKE | Single value | Checks if the custom field value is not similar to the compare value, using MySQL NOT LIKE operator |
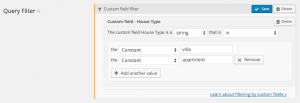
| IN | A list of values | Checks if the custom field value is within the list of compare values |
| NOT IN | A list of values | Checks if the custom field value is not within the list of compare values |
| BETWEEN | Two values | Checks if the custom field value is between the two compare values |
| NOT BETWEEN | Two values | Checks if the custom field value is not between the two compare values |
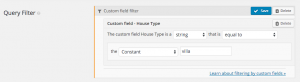
Compare value type
In order for comparison functions to work correctly, you need to tell Views what’s the data type you’re comparing to. For example, if your data type is a string, you must compare it to another string, to get the correct results.
Value types can be one of these:
| Data type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CHAR | Texts |
| NUMERIC | Numbers |
| BINARY | True / false |
| DATE | Dates |
| DATETIME | Date and time |
| DECIMAL | Decimal values |
| SIGNED | Signed decimal values |
| TIME | Time |
| UNSIGNED | Signed decimal values |
Source for compare value
You can filter according to constants (values that you determine when setting up the View), by time functions, by values that visitors will specify in custom searches, by time functions or by values set by Views shortcode attributes.
| Value source | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Constant | A value that you specify when setting up the View | For example, to choose only ‘featured’ posts |
| URL parameter | The value for the filter is set in the URL to the page | This will let you create custom searches filters for Views, where visitors can control what the View will show. |
| Shortcode attribute | The value for the filter comes from an attribute in the View shortcode | You’ll be able to insert the same View in different places and control content filtering via the View Shortcode. |
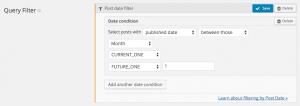
| NOW | The current time (in seconds) | Lets you filter content relative to the current time |
| TODAY | Today’s time (doesn’t change from hour 0 to hour 23) | Lets you filter content relative to the current day |
| FUTURE_DAY | TODAY + a number of days set in the second field | Lets you filter content relative a certain number of days from today |
| PAST_DAY | TODAY – a number of days set in the second field | Lets you filter content relative a certain number of days before today |
| THIS_MONTH | Current month (doesn’t change during the month) | Lets you filter content relative to the current month |
| FUTURE_MONTH | Current month + a number of months set in the second field | Lets you filter content relative to a future month |
| PAST_MONTH | Current month – a number of months set in the second field | Lets you filter content relative to a past month |
| THIS_YEAR | Current year (doesn’t change during the year) | Lets you filter content relative to the current year |
| FUTURE_YEAR | Current year + a number of years set in the second field | Lets you filter content relative to a future year |
| PAST_YEAR | Current year – a number of years set in the second field | Lets you filter content relative to a past year |
| SECONDS_FROM_NOW | Current time + a number of seconds | Lets you filter content relative to a future time, calculated in seconds from now |
| MONTHS_FROM_NOW | Current time + a number of months | Lets you filter content relative to a future time, calculated in months from now |
| YEARS_FROM_NOW | Current time + a number of years | Lets you filter content relative to a future time, calculated in years from now |
THIS_MONTH returns a value representing the beginning of the current month. In case that you want to get results from the whole current month, you should use a comparison like THIS_MONTH <= post_date < FUTURE_MONTH(1).2. Examples
3. More Reading
- Need to filter by date and time? Real more about Views date filters.
- Want to allow visitors to filter content? Learn about custom searches.